Author:Alan WangDate:2022-12-13

The biggest difference between electric vehicles and traditional fuel vehicles - Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles (ICEV) lies in the power system. The power source of electric vehicles is "electricity", while automobiles use "gasoline (diesel) oil" to burn This is why the car is called a "car".
From a structural point of view, the drive system of a car is an engine, which is a device that converts the chemical energy (heat energy) generated by igniting the fuel (gasoline and diesel) in the fuel tank into mechanical energy (kinetic energy) to drive the car; and the drive system of an electric car It is a motor, which is powered by the electricity in the battery to convert "electrical energy" into "kinetic energy". To put it simply, an electric vehicle replaces the fuel tank with a battery, replaces fuel with electricity, replaces the engine with a motor, and drives the motor with electricity to drive the wheels.
From the English "Electric Vehicle" literal translation of electric vehicles, it refers to electronic vehicles. In a broad sense, as long as a vehicle is equipped with a battery and motor system and powered by "electric energy", it can be called an electric vehicle (EV).
During the development and evolution of electric vehicles, many electric energy technologies have been developed to drive motors. Coupled with factors such as difficulties in battery research and development, battery power durability, and other factors, different forms of electric vehicles have been derived. The diversified types of electric vehicles can be roughly divided into the following types Three types:
1. Pure Electric Vehicle (BEV)
A battery electric vehicle (Battery Electric Vehicle, BEV) refers to a vehicle that is powered solely by a battery. The electric energy of the battery is used to drive the motor and the converter to replace the engine, and to perform the function of transmitting power. This is an electric vehicle in a general narrow sense, or called For pure electric vehicles.
Pure electric vehicles do not have an engine, do not need a fuel tank, do not need to consider the intake and exhaust systems, do not emit exhaust gas, and have no air pollution problems. With the rising awareness of environmental protection, they have gradually become the mainstream models developed and launched by most car manufacturers in recent years. Tesla, the world's most famous electric vehicle manufacturer, is a representative manufacturer of pure electric vehicles.
2. Hybrid Vehicle (HV)
A hybrid vehicle (HV), or hybrid vehicle, is a vehicle that uses two or more energy sources to generate kinetic energy, and may have two or more drive systems such as a gasoline engine and an electric motor. Commonly used energy sources are fuels (including gasoline, diesel, liquefied petroleum gas, etc.), batteries, fuel cells, solar cells, compressed gases, etc. Commonly used drive systems include technologies such as internal combustion engines, electric motors, and turbines.
1. Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
In hybrid electric vehicles (Hybrid Electric Vehicle, HEV), oil-electric hybrid is the most common, so HEV is also called oil-electric hybrid vehicle (abbreviated as oil-electric vehicle). Gasoline trams use both "gasoline engine" and "electric motor" power. However, ordinary gasoline trams are not charged through the power grid. The electric energy is generated by the engine and converted by recovering kinetic energy during deceleration. Therefore, when the electricity of the gasoline tram is low, the gasoline engine will automatically start to drive the generator to charge Therefore, there must be oil in the fuel tank of the vehicle, and it is not allowed to drive without oil.
Gasoline electric vehicles use electric motors to assist power when starting or driving at low speeds in urban areas. Compared with pure fuel vehicles, gasoline-electric hybrid vehicles consume less fuel, accelerate faster, and are relatively more environmentally friendly; The two power systems need to be equipped with fuel tanks, internal combustion engines and batteries, etc., which take up a lot of space in the car body.
For the development of hybrid electric vehicle technology, the founder of Porsche (Porsche) Ferdinand. Ferdinand Porsche (Ferdinand Porsche) is known as the pioneer of the development of electric vehicles. He invented an electric vehicle driven by two electric motors arranged on the front wheel hub. In 1901, this car was improved to generate electricity from a gasoline engine and supply power to an electric motor, which is regarded as the beginning of a gasoline-electric hybrid car.
However, the start of petrol trams sweeping the world was delayed until the end of the 20th century.
The story begins on January 16, 1992. On that day, Toyota Motor Corporation issued the "Earth Charter" (Earth Charter), declaring that it will develop low-polluting vehicles. In 1997, Toyota Motor successfully launched the world's first mass-produced car equipped with a gasoline-electric hybrid system, opening a new page for gasoline-electric vehicles in the 21st century. Toyota Motor has also become a representative of the world's leading and integrated gasoline-electric vehicle manufacturers.
2. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
With the evolution of innovative technologies, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle, PHEV) that can be refueled and recharged have been developed, or plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. The biggest feature of the plug-in hybrid vehicle is that it can be refueled, or it can be connected to an external power supply, and the vehicle battery can be charged from an external grid by using a charging station or household charging equipment; in other words, when driving in pure electric mode, it is like a normal pure battery. electric car. When the power is insufficient, the engine will automatically start and switch to gasoline-electric mode to continue driving, eliminating the anxiety of insufficient battery life.
Although the battery capacity of plug-in hybrid vehicles is larger than that of gasoline-electric hybrid vehicles, it is smaller than that of pure electric vehicles. The battery life is mostly only tens of kilometers, and it is mainly designed for short-distance commuting. If you want to drive long distances, you must rely on the internal combustion engine and use gasoline to assist. Therefore, plug-in hybrid vehicles rely less on charging stations, and are relatively environmentally friendly than fuel vehicles. They also have the convenience of gasoline and diesel vehicles, combining gasoline and electricity Two advantages.
3. Extended Range Hybrid Electric Vehicle (EREV)
There is also an extended range electric hybrid electric vehicle (Extended Range Electric Vehicle, EREV), which is an electric vehicle with increased mileage.
Similar to plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, extended-range gasoline-electric hybrid electric vehicles have a fuel engine, battery and electric motor at the same time, the fuel tank needs to be refueled, and the battery needs to be charged; The engine of an electric vehicle is to charge the battery to increase the mileage, and does not provide power output. The power source of the vehicle depends entirely on the battery and motor.
Extended-range gasoline-electric hybrid electric vehicle is an innovative design of General Motors in 2007 to solve the insufficient endurance of pure battery vehicles. However, after the improvement of battery technology and efficiency, GM has discontinued this type of extended-range gasoline-electric hybrid electric vehicle in 2019. Cars are gradually being replaced by pure electric vehicles.
3. Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
In addition, there is also a fuel cell electric vehicle (Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle, FCEV), which is an electric vehicle equipped with a fuel power generation device, which converts the chemical energy in the fuel into electrical energy. The common fuel is hydrogen, and the stored high-pressure hydrogen is added to the Oxygen in the air reacts to generate water, electricity, and release heat; other different fuel sources also come from any hydrocarbons that can decompose "hydrogen", such as natural gas, ethanol, and methane to generate electricity.
Generally, the battery modules of pure battery electric vehicles must be charged to operate, and charging takes time, but fuel cell vehicles are different, as long as "hydrogen" is added, they can be driven on the road, saving waiting time, and fuel cells only emit water and heat when generating electricity , so fuel cell electric vehicles are regarded as zero-pollution vehicles, which are truly energy-saving and environment-friendly vehicles.
Transition from fuel vehicles to new energy vehicles
As shown in Figure 2-1, four types of BEV, HEV, PHEV and FCEV are currently well known in the market. Traditional fuel vehicles are equipped with different power devices. These vehicles using new technologies and structures, also known as "new energy vehicles", are the new future of transportation vehicles.
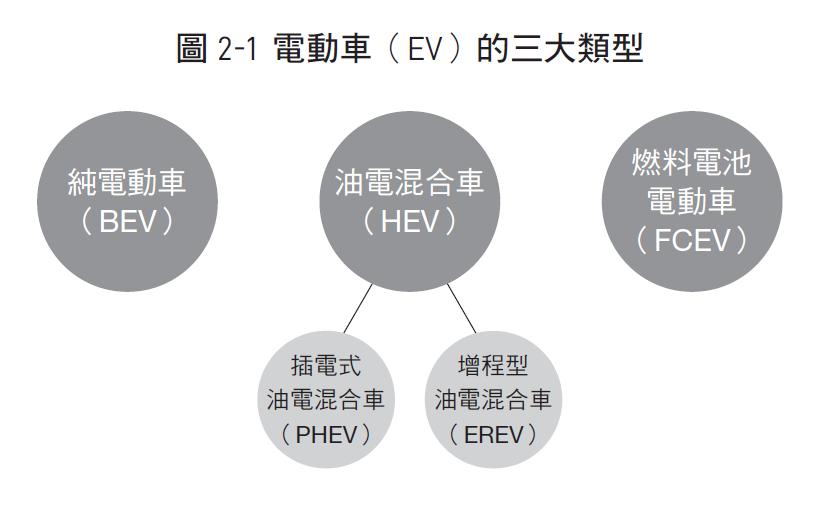
Due to the catalysis of environmental protection and energy saving issues, battery electric vehicles and gasoline-electric hybrid vehicles will gradually replace traditional fuel vehicles. In addition to the problem of exhaust emissions caused by internal combustion engine drive, we can get a glimpse of the whole picture from the characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
As listed in Table 2-1, there are obvious differences in structure between electric vehicles and fuel vehicles. In traditional vehicles, the internal combustion engine burns gasoline and diesel to generate heat and gas, which is converted into kinetic energy to run the vehicle. The engine generates heat when burning fossil fuels. Carbon dioxide becomes a greenhouse gas, which is an important source of environmental pollution.
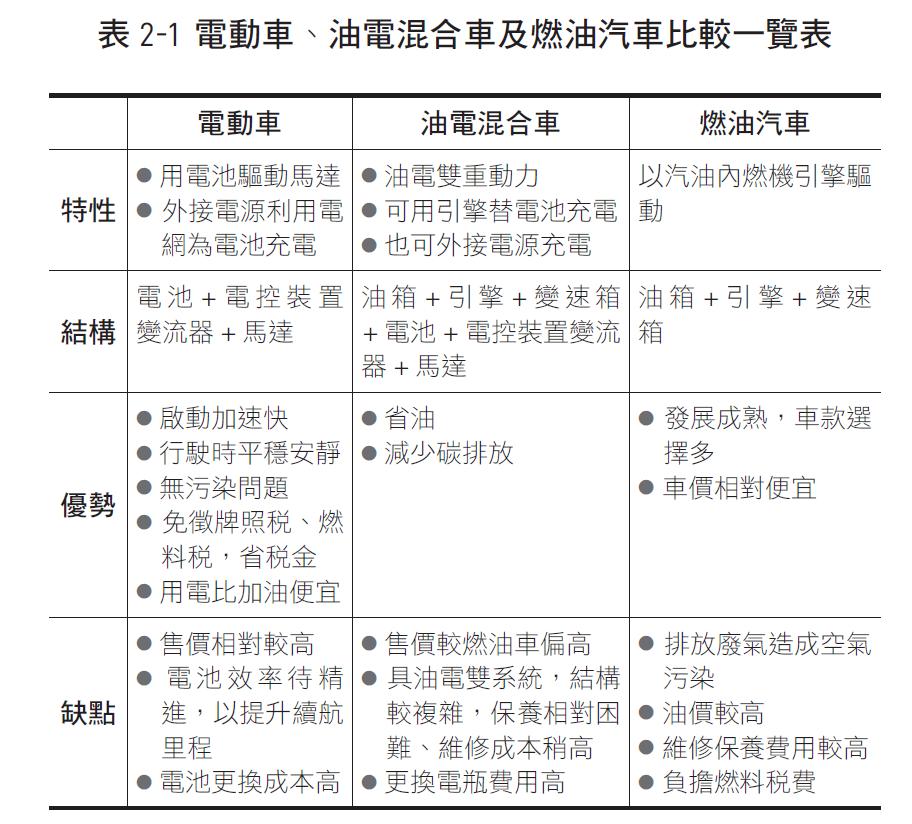
From the perspective of pure electric vehicles, the use of batteries does not require oil and reduces carbon emissions, but the batteries have a service life and the cost of battery replacement is relatively high. Different from the internal combustion engine of traditional fuel vehicles, the motors of electric vehicles run quieter and more smoothly. Some models are not even equipped with a gearbox, so there will be no vibration when shifting gears, smooth driving, comfortable rides, and explosive power when starting Strong and effective.
At present, the common types of electric vehicles on the market are mainly pure battery electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, accounting for more than 99% of the electric vehicle market. As for fuel cells, due to the high cost of materials, the price of fuel cell electric vehicles is unattainable, which is the biggest bottleneck in popularization. At present, the number of fuel cell vehicles is very small. Taking 2021 as an example, there will be only more than 50,000 hydrogen fuel cell vehicles in the world. Accounting for 0.3% of the total global EV fleet.
Fuel Cell (Fuel Cell) is a power generation device, just like a generator, as long as the fuel "hydrogen" is added to the gas storage cylinder to generate electricity through a chemical reaction, the power of the fuel cell can be maintained, unlike ordinary non-rechargeable batteries It can be thrown away after use, and it does not need to be continuously charged like a rechargeable battery. It is a veritable new energy source. In addition, fuel cells have the characteristics of low pollution, low noise, no charging, high efficiency, and long life. In recent years, the international research and development trend has been increasing.
↑Previous [
How to use charging piles safely? ]
↓Next [
The electrification transformation of new energy vehicles has broad prospects for future development ]









